Ваша заявка принята!
Наш менеджер свяжется с Вами
в течение 2 минут!
Рабочее время 8:00-17:00 (МСК)
We will be very happy to conduct a detailed comparative analysis of our installation and the installation from another manufacturer, it is important for us to note that, first of all, we differ not only in quality and perfect technology, but also in an individual approach, primarily based on the specific waste of the client, its morphology and features, chemical composition, aggregate state, our chemists will allow calculations, analysis, the results of which form the basis for the design and selection of the layout of the complex. This guarantees the client that he receives reliable data on the operational performance of his installation (equipment).
| № | Name of the characteristic | Waste thermal treatment and disposal unit (INCINERATOR) «BRENER-500-ECO-B», Parameters |
Equipment for high-temperature neutralization and waste disposal based on the HURIKAN 400 R incinerator with a dry gas cleaning system, Parameters |
Comments on ECO-SPECTRUM |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. About suppliers: | ||||
| 1.1. | Referent list | not represented | Confirmation (documents) of the availability of experience in designing and supplying rotary equipment with a gas cleaning system are provided in Appendix No. 1 (The reference list of delivered rotary-type incinerators with the contacts of operating organizations) |
For an objective comparison and a comprehensive analysis, it is necessary to establish the existence of experience in the production of rotary kilns, it is necessary to check each object with the supplied equipment |
| 1.2. | Confirmation of emissions compliance (analysis protocols from the rotary kiln) | no data provided | The documents confirming compliance with emissions are provided in Appendix No. 2 (confirmation of compliance with emissions of international standards) |
For an objective analysis and comparison of incinerator, it is necessary to obtain confirmation of compliance with emissions of international standards. It is necessary to request all data indicating the Description of equipment name of the incinerator, the application of the certificate of an accredited laboratory to the emission protocols |
| 1.3. | Availability of patents, confirmation of own solutions and technologies | no data provided | The documents confirming Patents for rotary incinerator lining, gas cleaning system (drop catcher) presented in |
For a comprehensive analysis and exclusion of risks associated with the acquisition of equipment manufactured in violation of the intellectual rights of competitors, it is necessary to verify the right to manufacture equipment |
| 1.4. | About company, production and financial resources of the supplier |
According to official sources of the tax service TIN 1840042015, name: LIMITED LIABILITY COMPANY PRODUCTION ASSOCIATION "ECOSYSTEMS" https://www.audit-it.ru/contragent/1151840007550_ooo-po-ekosistemy ______________ the number of employees in the state for 2022 is 8 people (an increase of 1 employer from 2021; income for 2022 is 125.9 million (decrease of 4% from 2021) Authorized capital: 10 thousand ₽ |
According to official sources of the tax service TIN 2312187206, name: LIMITED LIABILITY COMPANY "ECO-SPECTRUM" https://www.audit-it.ru/contragent/1112312011030_ooo-eko-spektrum _______________ the number of employees in the state for 2022 is 105 people (an increase of 32 employees from 2021), income for 2022 is 503,7 million (an increase of 66% from 2021) Authorized capital: 1.02 million ₽ |
it is necessary to request information and pay attention to the production and financial resources of the supplier company in order to obtain guarantees of solvency and availability of resources for order fulfillment
The ECO-SPECTRUM company The production of a high-tech product requires highly qualified personnel At the moment, the number of personnel in the ECO-SPECTRUM company is more than 120 people: production staff - 64 people, engineering staff - 35 people, administrative and support staff more than 20 people. |
| 2. About equipment: | ||||
| 2.1. Сharacteristics of the incinerator: | ||||
| 2.1.1 | Combustion Chamber Volume, no less | 4,2 m3 | 4,8 m3 | |
| 2.1.2. | Combustion Chamber, Weight | no data provided | 11 ton | |
| 2.1.3. | Combustion Chamber, Lining, thickness | Refractory concrete Thickness- no data provided |
Composite: refractory concrete and ceramic plate, 120 мм (30mm -ceramic fiber plate 90mm -concrete) |
|
| 2.1.4. | Afterburning Chamber Volume, no less | 4,2 m3 | 6 m3 | To ensure a guaranteed gas delay of 2 seconds at nominal capacity |
| 2.1.5. | Afterburning Chamber, Weight | no data provided | 2,5 ton | |
| 2.1.6. | Type of afterburning chamber | Rectangular | Cylindrical with radial inlet | Provides 100% utilization of the entire volume of the chamber during the afterburning of gas |
| 2.1.7. | Afterburning chamber lining, thickness | Refractory bricks Thickness- no data provided Material lining of the chamber ceiling- no data provided |
Ceramic Fiber Thickness 120-140 mm Material lining of the chamber ceiling- Ceramic Fiber |
|
| 2.1.8. | Fire-resistant properties of heat insulation, °C | 1700 °C. | The operating temperature of: refractory concrete is 1400 C, refractory coating of the insulating fiber is -1700 C, the insulating fiber is 1260 C |
|
| 2.1.9. | Сalculation model of lining types | Appendix No. 3 (calculation of thermal conductivity) To compensate for the heat loss of fireclay bricks, fuel consumption for maintaining high temperatures will increase in 3 times as in comparison with the insulating layer, whose heat loss is 3 times less The use of insulating material in bricklaying is impossible due to the loss of stability of the lining |
||
NOTE! |
For the variant with fireclay brick lining, the average heat transfer value will be from 5 to 10 W/(m2 * ° C), depending on the brand used | The heat transfer for the main chamber of the HURIKAN R series incinerator is 2.9 W/(m2*°C), the heat transfer of the secondary chamber is 2 W/(m2*°C). | Incorrect characteristic or false. Insulation with such characteristics is not available on the market at all (with an operating surface temperature of 1700 C), perhaps the supplier means a refractory fireclay brick. Regarding its characteristics, see paragraph 2.7.-4 colomn | |
| 2.1.10. | Element seal of the loading unit of the rotary kiln | NO | The use of a petal seal on the main chamber of the incinerator allows for maximum tightness, to exclude extraneous air intake, and also to exclude the operator's contact with the incinerator flue gases while ensuring the required mobility of the chamber (minimal friction and, accordingly, energy consumption for the drive). | |
| 2.1.11. | Afterburning Chamber, Weight | no data provided | не более 2500 кг | |
| 2.1.12. | Combustion (main) chamber temperature, regulated, °C | 850 °C | 850-950 °C | |
| 2.1.13. | Afterburning chamber temperature, regulated, °C | 850-1000 °C | 950-1150 °C | |
| 2.1.14. | Burn Rate, kg/hour (up to) | 1000-2000* * Depends on calories and waste density |
400 For waste with a specific heat of combustion of 2000 kcal/kg and a humidity of 35% |
The incinerator's capacity of 1000-2000 kg/hour is possible on inert waste with zero caloric value (for example, sand, soil), that is, this indicator is the capacity of the rotary kiln - to pass inert material during rotation. |
NOTE! |
the specified productivity (1000-2000 kg / hour) on waste with this configuration of the complex is impossible. The client must provide a list of waste to determine the chemical. composition and, accordingly, performance. Otherwise, the comparison of characteristics will not be objective and correct. Сморите таблицу с расчетом. | Burn rate calculated on the HURIKAN 400 R rotary type unit for different types of waste (taking into account the thermal conductivity values of lining materials) Appendix No. 4 (Fuel consumption and burn rate) |
||
| 2.1.15. | Average loading capacity =" Volume "of one-time loading, m3 (up to) (receiving hopper with screw feed to the combustion chamber) | 1.5 м3 | From 1 to 2 м3 | The storage hopper with subsequent screw feeding can be supplied with almost any volume, it all depends on the type of waste, it is agreed with the Customer |
| 2.1.16. | Additional loading opening (mm), w/h | 500х500 | Absent (impractical) | Optionally, it is possible to install a manual feeding unit built into the hopper, however, we consider it impractical, the design of the loading unit, where static and rotating parts are joined, will not allow this window to be used functionally, efficiently and safely. |
| 2.1.17. | Liquid waste supply port | no data provided | liquid waste supply port is installed on request | Depending on the characteristics of the liquid waste, we can choose a feed unit |
| 2.1.18. | Fuel type | Diesel | Diesel | It is possible to supply burner devices for any type of fuel by agreement |
| 2.1.19 | Burner devices Total capacity of burner devices |
3 pcs (Eco Flam, Italy) no data provided |
4 pcs (Ecoflam, Italy) Total heat output Min. 219 -Max.679 kW |
Depending on the thermal conductivity of the lined layer, the total thermal power of the burner devices is selected |
| 2.1.20. | Diesel consumption, liters per hour, min-max | 20-60* * Depends on calories and waste density passport fuel consumption, waste consumption is not specified |
25-68 kg/h Fuel consumption according to passport Fuel consumption passport means the consumption of fuel by burner devices per hour during non-stop operation |
Due to the unique combined lining of the combustion chamber and the afterburning chamber with high insulation and refractory characteristics, fuel consumption is reduced to almost zero.( Patent No. 1234567) When the customer provides a list of waste, we can calculate the burn rate and fuel consumption For example, fuel consumption for medical waste /solid waste |
| 2.1.21. | Method of waste loading | From the top | From the top | |
| 2.1.22. | Separation of ash |
no data provided | YES | |
3.1.Gas cleaning system |
||||
| 3.1. | DRY and WET gas cleaning system | YES | DRY WET COMBO |
|
NOTE! |
There is no detailed data on gas purification technology and assembly of units | |||
| 3.2. | Cyclone filter | YES | YES | |
| 3.3. | Exhauster capacity, | 10000 m3/hour | 2500 Nm3/h (4300 m3/h at flue gas temperature +200°C) | |
NOTE! |
This parameter must be specified either at operating temperature or under normal conditions | |||
| 3.4. | Cooler (recuperator) | NO | YES | Provides pre-cooling of flue gases to operating temperatures to ensure the operability of the subsequent equipment of the gas cleaning system |
NOTE! |
Without reducing the temperature in the system, the service life of cyclones made of black metal will burn out within 3-5 months | Reduces to 200 S (a necessary element of the gas cleaning system to ensure the operability and long service life of the equipment) | ||
| 3.5. | Cleaned gases temperature (at outlet to atmosphere), °C | no more than 200 °C | no more than 200 °C | |
NOTE! |
Temperature reduction from 950 C to 200 C in the configuration presented by BRENER is possible only with forced dilution of flue gases with atmospheric air | The temperature reduction from 1150 C to 200 C in the ECO-SPECTRUM configuration is achieved due to the heat exchanger, HURIKAN never uses forced dilution of flue gases with atmospheric air, as this distorts the emission concentrations and contradicts environmental legislation. | Ensuring truthful indicators of plant emissions, there is no distortion of concentrations Forced dilution of flue gases with atmospheric air distorts the readings of the concentration of substances in the exhaust gases, which is fraught with violation of environmental control |
|
| 3.6. | Overall size of the cyclone Temperature of gases in a cyclone |
no data provided no data provided |
LxWxH, mm - 1300x700x2600 200 C |
|
| 3.7. | Drop catcher | NO | YES | Necessary for removing liquid and moisture (especially if there are liquid or wet inclusions in the waste) for the bag filter and ensuring its operation Removes excess moisture that is formed when condensation occurs due to the cooling of the flue gas. Protects the bag filter from failure. |
| 3.8. | Bag filter for capturing fine suspended particles | NO | YES | Provides removal of fine fraction of suspended particles |
| 3.9. | Adsorber for gas purification from gaseous impurities and heavy metals | NO | YES | Provides purification from gaseous impurities and heavy metals |
| 3.10. | Bypass with emergency pipe | NO | YES | Ensuring the safety of operation in case of emergency situations with the gas cleaning system |
| 3.11. | O2 and CO sensor to control chemical afterburning | NO | YES | Provides control of the neutralization process with the maintenance of the required excess air and the level of chemical afterburning within the permissible norms of gas purification |
| 3.12. | Exhauster power supply | 380V | 380V | |
| 3.13. | Chimney stack diameter, mm | 400 | 500 | |
| 3.14. | Chimney stack height, meter | by your request | by your request | |
| 3.15 | Operation dimensions, meters (up to) | 11.5x3х3.2 | 24,4х3,5х6,3* | In height, the minimum size, taking into account the emergency chimney |
| 3.16 | Total weight, tons (up to) | 28 | 40 two containers: 30 -foot и 10-foot |
|
NOTE! |
With such a size, the gas cleaning equipment system and the installation cannot provide the declared performance | |||
4.1. Automatization |
||||
| 4.1. | Automated digital control panel (touchscreen) IP 65 | YES | YES | The degree of dust and moisture protection of the control panel is IP65. |
| 4.2. | Combustion process | Automated no detailed data provided |
Automated Discharge sensors Temperature sensors Oxygen sensors Pressure gauge Differential pressure gauge PH sensors Fuel monitoring sensors Etc. |
HURIKAN 400 R Automatization The control is carried out in automatic mode by burners (simultaneous switching on and differentiated separately), setting temperatures to save fuel and control the combustion process. Display of setpoints and actual values. Indication of errors and accidents. Graphic touch display, built-in archiver. Indicators for monitoring the status of burner devices. Monitoring the status of all sensors, pressure sensors. Indication of the emergency state of the installation, excess of operating temperatures. Automation of loading and opening of the hopper lid, separation of ash by fractions. Counter for the duration of the installation (operating hours). Displays the current fuel level in the fuel tank. Blocking the operation of the burner device when the fuel level is low. Auxiliary light and sound alarms. Remote operator panel with color touch multi-touch LCD display for remote control. Application of remote access technology to the controller: control, viewing, changing data on the PLC in remote mode from the operator's PC |
5.1 Consumption and electricity |
||||
| 5.1. | Total power consumption, kW (up to) | 35 kW | 66,5 kW (Incinerator- 11.5 kW- rotation drives and deashing system ) Heat exchanger and Dry gas cleaning -55 kW |
The gas neutralization temperature should be at least 950-1150 C, however, in the absence of any heat exchangers, it can be concluded that the cooling of flue gases before the cyclone occurs due to dilution of combustion products with atmospheric air, but in this case energy consumption should be higher than stated (35-55 kW) due to an increase in gas volumes after stirring with air by a fan. At the same time, it should be noted that no fan works at high temperatures, and if air stirring occurs due to traction, then it is safe to say that gas cooling from 950 C to 200 C is impossible. Also look at paragraph № 2.26.1 |
| 5.2. | Power supply | 220-380V/50-60Hz | 220-380V/50-60Hz | |
1.Main chamber -1,
2.Afterburning chamber-1
3.Waste receiving chamber-1
4.Loading hopper (screw)-1
5.Ash unloading (screw)
6.Ash unloading (manual)-1
7.Belt feeder-1
8.Gas cleaning system-1
1.Main chamber -1,
2.Afterburning chamber-1
3.Waste receiving chamber-1
4.Loading hopper (screw)-1
5.Ash unloading (screw)
6.Ash unloading (manual)-1
7.Belt feeder-1
8.Gas cleaning system-1
9.Ash unloading (screw)
11.Ash unloading (manual)-1
12.Belt feeder-1
13.Gas cleaning system-
14.Ash unloading (screw)
15.Ash unloading (manual)-1
16.Belt feeder-1
17.Gas cleaning system-1
For a comprehensive analysis, it is necessary to resort to recommendations, namely, to request the missing information:
Recommendations
1) The caloric content and humidity of the waste, on which the productivity of 1000-2000 kg / hour is established.
2) The number of burner devices and their name (models), manufacturer
3) The amount of fuel consumed at the declared technical characteristics per 1 kg of incinerated waste
4) Length and diameter of the furnace pipe
5) Incineration chamber in section with lining indicating:
5.1. Thickness and grade of steel
5.2. Thickness and lining material
5.3. Lining fasteners
6) Lining of the roof of the afterburning chamber
7) Weight of the combustion chamber
8) Afterburning chamber weight
9) Total capacity of the burner devices
10) The volume of flue gases at a capacity of 1000 kg / h, m3/ h, specify the composition and dimensions of the cyclones of the gas purification system - specify which filters -specify the reagent consumption -specify the consumption of adsorbents -specify the water consumption -specify the volume and composition of the waste of the Gas cleaning system
11) Detailed functional description of automation with indication of the name of sensors and PLC
12) Specify the service life of gas cleaning
13) Due to which the exhaust gas is cooled, at which node the temperature drops
14) A reference list of existing rotary kiln facilities with a gas cleaning system, indicating contacts and company names for feedback
15) Photos or videos of the operation of similar equipment
16) Indicate what emissions of substances will be at the output with the declared characteristics
17) Indicate the overall size of the cyclone
Influencing factors on the amount of fuel for waste incineration
The process of thermal neutralization and disposal of waste is carried out with constant or temporal use of fuel. Waste incineration is also possible without the use of fuel under conditions of constant continuous supply of waste to the main chamber. In this paper we’re going to find out what factors effect on fuel consumption and the functional mode of burners.
The first factor is what type of fuel will be used. There are several types of fuel used for waste incineration: diesel, gas, waste oils, fuel oil, etc. The calorific value of one type of fuel will be different from another. For instance, natural gas is more calorific compared to diesel, which means that gas consumption will be less than diesel consumption.
The second factor affecting the amount of fuel consumption is the calorific value of the waste. The higher the calorific value of the waste, the less fuel will be required for combustion (high-calorific waste is capable of sustaining self-combustion). To minimize or reduce to zero the consumption of fuel required for evaporation of water in the waste, heating to set temperatures and the cost of heat loss, possibly by the heat released by the waste. For example, the calorific value of contaminated plastic is more than 6000 kcal/kg, the calorific value of food waste is about 800 kcal/kg. So, unlike food waste, plastic can be burned without using fuel.
The third factor is the amount of air supplied to the main and secondary chambers. If the air is supplied without preheating, i.e., taken directly from the environment, that requires a significant amount of heat to heat it up to the preset temperatures. Consequently, the more air oxygen is required to burn the waste, the greater the fuel consumption for heating it. The more organic compounds in the composition of the waste, the more amount of air for waste incineration will be required. For example, the burning of 1 kg of contaminated plastic requires stoichiometrically about 9 kg of air, the burning of 1 kg of food waste requires about 2 kg of air. However, plastic is more calorific and the heat released during its combustion is sufficient to compensate the temperature loss.
The fourth factor is the size of equipment for thermal treatment and disposal of waste. The larger the unit, the more fuel will be needed to heat up the main and secondary chambers. For instance, there will be 4 kg/h of fuel consumption because of heat losses on the pressure vessel walls of the HURIKAN 150 incinerator, and 15 kg/h for the HURIKAN 1000 incinerator. At the same time, when the incinerator enters the operating mode, i.e., full heating and maintaining of a constant continuous supply of waste to the main chamber, the effect of size of equipment on the amount of fuel consumption is reduced due to different productivity: the more waste is burned per unit of time, the more heat is released, therefore, a more productive plant generates more heat.
Thus, the amount of fuel consumption for waste incineration is variable, and depends on a number of factors. The fuel consumption can also be minimized or reduced to zero.
Eco-Spectrum produces three models of incinerators, which are divided into chambered incinerators of Volkan series, chambered incinerators of Hurikan series and rotary incinerators of Hurikan series. The fundamental difference between chamber incinerators and Hurikan is the productivity and volume of incinerated waste. Volkan series differ in loading volume, while the performance does not change (from 45 to 75 kg per hour), and the index in the name of the incinerators (150, 200, 750 ...) indicates the volume of a single load. Hurikan series are characterized by high performance, achieved due to the presence of grates and the volume of the afterburning chamber of gases. The grate system developed by our company allows to increase the area of combustion of waste, thereby achieving high productivity. Combustion system is designed in our company. The index of incinerators of Hurikan series indicates the performance of the incinerator (70, 150, 300 ...).
Rotary Hurikan series are a rotating lined drum that allows the disposal of liquid waste, such as oil sludge, waste oils, etc., in addition to solid waste. Due to rotation, the waste is mixed, thanks to which a certain productivity is achieved on certain types of waste, which a chamber furnace cannot provide.
The technology of waste and waste gases neutralization after waste neutralization has been approved by a positive conclusion of the state expertise of the federal agency of Rosprirodnadzor. Eco-Spectrum regularly analyzes the ash obtained after waste disposal, as well as testing of equipment for emissions at customers' operating sites is carried out on an ongoing basis.
Incinerator installations designed by our company meet all international standards of environmental and sanitary safety. Environmentally friendly emissions are provided by correctly calculated gas afterburning chambers and gas filtration systems. Thermal neutralization of exhaust gases in the afterburning chamber of gases occurs at temperatures exceeding 1100 degrees, which meets all international standards and ensures effective burning of dioxins and furans.
First of all, the Eco-Spectrum acts as an expert in solving waste disposal issues, has extensive experience in the production and installation of incinerators, as well as a large number of projects in the field of equipment development and design.
The company's engineers, in cooperation with the company's environmentalists, as well as with university researchers, develop non-standard solutions for individual orders of their customers.
An absolutely open approach to the client: we never overestimate performance indicators, but work to improve quality, investing all available resources in professional development, personnel development, training of leading engineers, due to which our developments are among the most high-tech in the industry.
Disadvantages of bricks:
Advantages of concrete:
The composition of fly ash produced by conventional and clean burning can be characterized using the recommended testing methods and further characterized using the chemical tests in the table.
The buyer (customer) may specify the limit values of fly ash composition, depending on the specific features of a particular variant of its secondary (final) use.
Table 1 - Composition of ash and recommended chemical tests of ash
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Additional chemical tests (limit values to be set by the buyer/customer only if necessary) of fly ash
Table 2
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
In the case where the limit values are not set by the buyer (customer), the values laid down in the relevant regulations, including GOST R 54204, GOST 12596, shall apply.
The ash from the thermal waste decontamination can be further tested at the buyer/customer request with the appropriate physical tests given in Tables 1 and 2.
Additional mechanical tests (to be specified only at the request of the user) of ash and residues from waste incineration.
Table 3
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Fly ash certification testing and control
After the ash samples have been generated, certification tests are carried out to assess (confirm) the conformity of the ash characteristics required for its further use.
Acceptance criteria can be agreed and documented individually by the producer (who has produced the fly ash residue) and the user, depending on its possible end use, and it has to be considered that fly ash may contain some impurities that will affect the end use possibilities of the fly ash and the performance of the processes.
Certificates of conformity are issued based on the results of tests on ash dust samples. The supplier shall, on the buyer’s request, provide certificates of conformity with batches of fly ash dispatched from the place of generation.
If requested by the purchaser, ash sample test results are sent after test burns to the buyer as soon as they are available. Eco-Spectrum conducts a full range of research and develops recommendations for the further use of ash.
Recommendations apply to ash or other combustion products from combustion:
- household, industrial or commercial waste;
- sewage sediments or other newly generated waste;
- wood and wooden waste;
- rice bran;
- agricultural waste;
- sludge from the gas scrubbing unit;
- any combination of the above.
Ash disposal. The waste to be treated in the unit may contain refractory, non-combustible substances that pass into ash. Their presence affects the ash content: volume and quantitative chemical analysis. Thus, the amount of ash residue can be 3-50%, depending on the loaded waste composition. The output control serves to determine the physical and chemical properties and hazard class of the decontaminated material.
As SMR ashes and residues from waste incineration HS code 2621100000
After thermal waste decontamination of (incineration), secondary waste is generated according to the FCCW:
- 6 11 910 01 49 4 ash from burning sunflower husks;
- 6 11 910 02 49 5 ash from the burning of rice husks;
- 7 42 211 11 49 4 ash from the burning of bark and wood waste and sewage treatment sludge from pulp and paper production;
- 7 46 311 11 40 4 ash from the burning of dewatered sludge of domestic and mixed sewage is low-hazard;
- 7 47 112 11 40 4 ash from the burning of consumer waste in production, similar to municipal waste;
- 7 47 119 11 40 4 ash from the burning of consumption waste in the production, similar to municipal waste, mixed with industrial waste, including oily waste;
- 7 47 813 01 40 4 ash from the burning biological waste from the vivarium and laboratory animal waste;
- 7 47 821 01 40 4 ash from combustion of biological waste from animal housing, slaughter and processing;
- 7 47 841 11 49 4 ash from medical waste incineration, containing mainly silicon and calcium oxides;
- 7 47 911 11 40 4 ash from the combustion of waste paper, cardboard, wood and wood products, containing mainly calcium and magnesium oxides;
- 7 47 911 12 40 4 ash from burning cotton dust, waste paper, cardboard, and wood
- 7 47 931 01 40 4 ash from burning paper, cardboard, wooden containers (packaging) from explosives, pesticides, agrochemicals and other chemical products;
The resulting scale (ash) after processing can form a secondary raw material. The resulting secondary raw materials can be used as a mineral additive or filler in the manufacture of heavy, light, cellular concrete, dry building mixtures, as well as mineral binders for the preparation of mixtures and reinforced soils in road construction. The final consumption of SMR will be: production of foam and gas blocks, ash bricks, paving stones, production of cements and dry building mixes of concrete and piece reinforced concrete products, drainage devices, tiles, production of waterproofing and soundproofing materials, mineral fiber, various composite materials, mastics, sealants, and paint and varnish products, act as a filler in road construction, runways, taxiways, parking lots in airports, in the construction of port facilities, to increase the seismic resistance of buildings and structures, reclamation of quarries, in the construction of landfills, landfill bunding, dumping in garbage dumps, tailings, sludge reservoirs, dams, industrial pools and channels; filling of mined out spaces with ash. (Appendix 2).
If the obtained ash is used for decontamination of the waste containing toxic and ecologically dangerous substances, pelletizing technology is applicable: mixing of 40-60 wt.% of ash, 10-20 wt.% of silicon oxide component of SiO2 — 50-75%, Al2O3 — 530%, Na2O — 5-20%, CaO — 1-10%, 20-40 wt.% of acid component. From the obtained mixture, granules are formed, powdered with dispersed refractory material, dried and heat-treated in two stages: for 10-30 min at 400-600 °С and for 1-20 min at 870-950°С. Technical result: increasing the strength, water resistance of the obtained non-toxic pellets of non-toxic form, and the suitability for safe burial or application. Such a method has been patented as a method of producing ash-filled polymer concretes when high-molecular-weight compounds, such as unsaturated polyester resin, are used as a binder. Such polymer concrete is characterized by high strength characteristics, resistance to chipping, products from it have a pore-free surface.
One way to process ash with a specific surface of 2000-4000 cm2/g, containing salts of heavy metals — cadmium, copper, lead and zinc, mixed with sulfur in a ratio of 1:1-1:2.5 and heated to mastic consistency, after which the mastic is poured into molds for making blocks, or fed to the machine for pelletizing. When testing the samples, in aqueous extracts, zinc, cadmium, copper was not detected, lead — 0.024 mg/l, the content of petroleum products did not exceed 0.1 mg/l, hydrogen sulfide is not released.
Acid ash should be used to partially or completely replace porous sands and reduce the average density of concrete. For structures of underwater and internal zones of hydraulic structures type IV acid ash should be used.
In general, the disposal of ash in the composition provides recycling into environmentally safe products up to 90% of the original mass of ash.
The use of ash as a reclamation agent for mine and quarry workings during mining for the purposes of environmental protection and sanitary and hygienic direction of their reclamation according to GOST 17.5.3.04-83.
At low pH values (less than 5) liming with calcium-containing reagents is used: calcium oxide CaO, calcium oxide Ca(OH)2, and limestone flour (dolomite). At high pH values of initial raw materials (more than 8.5), deoxidation with Phosphogypsum is used. Sorbents and structurizers (pore-forming additives) are used to increase porosity and improve the structure of techno-soil.
The possibility of obtaining amorphous silicon dioxide (ASD) makes it possible to use the inorganic potential of rice husk as a raw material: SiO2 — 80 %, carbon C — 9 %, oxides (Fe2O3 - 0.01 %, Al2O3 — 0.15 %, TiO2 — 0.01 %, MgO - 0.4 %, CaO - 0.98 %, K2O — 2.09 %, Na2O — 0.07 %, Mn3O4 — 0.28 %, SO3 — 0.8 %), moisture capacity — 2 %, obtained at high-temperature (600-800°С) influence on the rice husks in a vortex flow of hot oxidizing gas. It has high thermal insulation properties, high melting point, low bulk density and high porosity. It is used in the steel industry to slow down the cooling of metal by insulating its surface. The coating absorbs non-metallic inclusions (aluminum oxides) in the liquid steel.
Return the decontaminated soil into the economic turnover or the environment by improving its biological properties by introducing biogenic elements. Biogenic elements are applied in the form of agrochemicals — nitrogen-containing mineral fertilizers (ammonium nitrate, potassium nitrate, urea, phosphate fertilizers, potash) fertilizers included in the state catalog of pesticides and agrochemicals approved for use in the Russian Federation.
The heat or materials resulting from these technologies can be used for various purposes or not used if it is not profitable for economic or organizational reasons.
It is possible to get material SMR (ash, decontaminated soil) product quality certificate (voluntary certification).
CN FEA Code 2621100000. Ash and residue from the burning of municipal waste.
It is possible to remove the generated heat energy not only by means of heat exchangers. The optimum solution considered is a combined heat and power generator that can utilize the waste heat of exhaust gas streams from 250°C to generate more than 600 kW of energy. The use of units in conjunction with modern thermoelectric generators (combined heat and power plants) eliminates the use of climate-damaging refrigerants as the working body using ethanol as the working body, in addition to the drive motor energy and highly efficient conversion of waste heat into electricity, compressed air, cooling.
Such a solution offers the user without affecting production:
• produce demand-oriented energy: the necessary quantity and quality of energy;
• higher efficiency: very low conversion losses;
• useful heat that can be used for heating or drying/preheating;
• useful heat can be converted into technical cold.
An alternative solution for heat generation can be the installation of a utilizing boiler, which converts the steam obtained into electrical energy. In addition, a condenser can be used for water cycling, or the use of waste steam to heat water at the enterprise. Then the exhaust gases if necessary, go to the gas scrubbing unit.
The sequence of processes for generating electricity by converting heat for this purpose is similar to that in diesel and gasoline power generators. Conversion of heat released during thermal decontamination into mechanical energy. Electricity is generated in the generator.
A popular type of generating set is its modification with autostart. The thermoelectric generator turns on automatically without operator intervention in case of an interruption of the circuit in the central power supply system. The equipment can be used:
• as a backup power supply;
• as the main supplier of energy;
• for seasonal activation of the facility.
The recuperator unit makes it possible to heat water with the waste gases from the VOLKAN or HURIKAN Series to a temperature sufficient for heating the production facilities or for hot water demand in the plant.
Concentrated effluent from the gas scrubbing system and wastewater from process equipment washing can be used for ash cooling with steam removal to the firing unit.
- VOLKAN Series: heat output in water or air — from 8000 kcal/h to 120,000 kcal/h; electricity generation — generator capacity from 3 to 25 kW.
HURIKAN Series: heat output in water or air — 8000 kcal/h up to 0.82 Gcal/h; power generation — generator capacity from 3 kW up to 250 kW.
HURIKAN R Series: heat output in water or air — 8000 kcal/h up to 5.16 Gcal/h; power generation — generator capacity from 3 kW up to 2,5 kW.
Recuperators are calculated and manufactured individually according to the specifications and the customer requirements, which takes into account the length of the heating duct, the area of heated rooms, etc.
In developing recommendations for thermal decontamination and ash use, Eco-Spectrum uses the results of its own research, R&D results, R&D, as well as the following regulations and standards :
Eco-Spectrum provides full warranty service for the entire warranty period. Eco-Spectrum guarantees:
- ensure equipment maintenance and repair when used for its intended purpose throughout the warranty period;
- make repairs, replace low-quality equipment, its parts with high-quality equipment with better characteristics within the Customer agreed period.
During the warranty period, any faults detected will be repaired at the place of equipment location and, if necessary, at the place of warranty service.
All spare parts, which ECO-SPECTRUM installs on the equipment during the warranty period, have functional characteristics according to the technical documentation of the equipment, compatible with the original accessories. The costs associated with the defect elimination in the equipment during the warranty period shall be borne by ECO-SPECTRUM.
- technical data sheet for all units of the equipment; operating instructions for the equipment;
- a complete set of technical documentation, including: data sheet, technical operation manual, including data sheets and operation manual for purchased products used in the equipment, technical documents on the operation of instrumentation and automation, maintenance program, performance testing and preventive maintenance schedule, certification documents on compliance with fire safety (when distributed to the object of purchase);
- executive documentation in accordance with the requirement of SP 77.13330.2016, SP 76.13330.2016 (if provided for in the contract);
- detailed documentation, which includes a wiring diagram;
- declaration of compliance with the technical regulations of the Customs Union;
- valid positive State Environmental Expert conclusion on the project of technical documentation and technology of waste decontamination and disposal (certified document copies);
- operation manual provides recommendations on how to prepare the waste before loading;
- other documents to ensure uninterrupted and accident-free operation, stipulated by the current legislation of the Russian Federation: acoustic characteristics, protocols of noise measurements.
- analysis protocols issued by an accredited laboratory, confirming compliance with the emission standard for polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins and dibenzofurans not exceeding 0.1 ng/m3;Operational and accompanying documentation must be provided in Russian, and in English for export deliveries. All operating systems are also programmed in the language of the customer's country.
Supervision and installation is performed directly by the supplier's managers. The working staff is provided by the buyer, and the main components are controlled by specialists of the operating company.
Under the guidance of the company's specialists, the customer's employees perform the entire installation: make adjustments, setting of the main parameters, their adaptation to the appropriate requirements.
The customer prepares the site, erects foundations or bases for the complex, installs utilities to the site, and carries out other work as specified in the project.
High-capacity mobile complexes for waste disposal in places of temporary storage (e. g. pesticides, construction waste, landfills, etc.) are quickly deployable compact complexes of high performance (unit movement is possible in hard-to-reach places, due to the unique technology, the lining is stable and not subject to destruction).
The unit provides:
· ability to move the complex to a place of waste generation or temporary storage;
· rapid deployment in case of emergency measures to eliminate the consequences of emergencies, spread of epizootics, etc.;
· autonomy due to the placement of fuel tanks, generators and other equipment on the landing platform (for autonomous operation in the field);
· due to special fasteners and quick-release mechanisms, all attachments are quickly assembled and disassembled;
· high productivity due to the grate zone and increased combustion area.
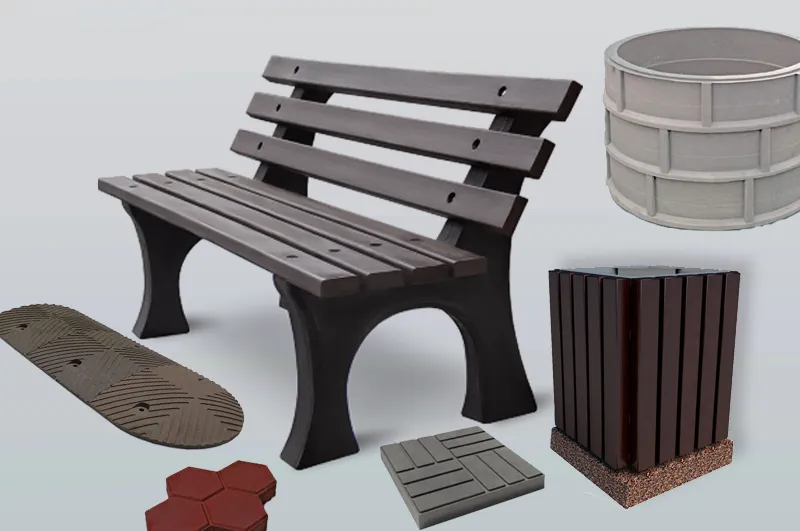





The unit provides:
• ability to decontaminate waste continuously 24/7;Ash disposal. Waste sent for processing may contain refractory non-flammable substances that pass into ash. Their presence affects the ash content: residue mass and composition. Thus, the ash residue amount depends on the loaded waste composition. Outlet ash control is necessary to determine the physical and chemical properties and hazard class of the decontaminated material.

Earlier studies of ash show is composition domination by silicon and calcium oxides, which implies that the main area of ash application can be the construction field — use as an inert building material.
HURIKAN 1000 unit provides:
• possibility of mechanized loading of oversized waste;• The unit provides decontamination of dioxin and furan emissions during thermal decontamination of chlorine-containing waste, safe working conditions for the operator due to automated loading of waste with dosing.
• Lining allows high combustion chamber temperatures to be maintained, reducing fuel consumption and extending unit life by years.
• The wet scrubbing system captures volatile gases from the decomposition of highly hazardous toxic waste.
• Closed cycle of water use through the water treatment unit, no contaminated effluents and reduced water treatment
Advantages:
- higher scrubbing efficiency than for dry ones;
- gas quenching with abrupt cooling, which prevents recombination of dioxins and furans;
- less waste after the scrubbing system than for dry system.
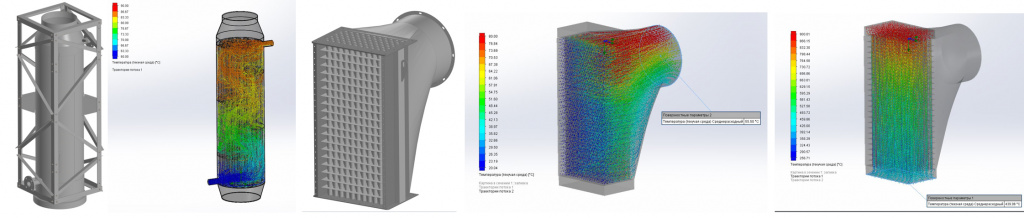
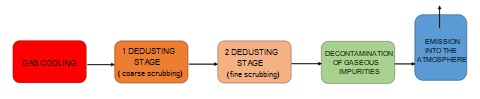
The gas scrubbing line itself must have at least two stages: coarse and fine scrubbing (Fig. 1).
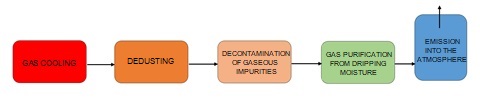
Fig. 1 Process diagram of the wet gas scrubbing system of the incinerator
The TDU has no lining layer to provide and maintain the stated temperatures in the chambers. Even in the case of structural "pipe-in-pipe" design, the inner tube will be exposed to temperatures that exceed the thermal resistance of the material, which will cause significant deformation, loss of bearing capacity, corrosion, and burning. Steel AISI 430 (lining chambers) is used up to +850°C, with prolonged use in the range of +400°C - +600°C becomes brittle, fragile and requires annealing for further use.
Significant heat losses not only increase fuel consumption to maintain decontamination temperatures, but also expose other structure elements to heat, degrading performance, reducing load-bearing capacity, increasing wear (supports, bearing assembly, etc.).
The HURIKAN 2000R incinerator has a double-layer lining of both the combustion and the afterburning chambers.
The combustion chamber lining (together with the loading and unloading unit) consists of:
1. Insulation of internal walls of the furnace body with fiberglass refractory slabs is arranged to reduce heat loss, ensure stable temperatures, minimize fuel consumption to maintain combustion, avoid high thermal loads on the metal body, increase efficiency and the service life of the unit. Heat resistance up to 1260°C.
2. Monolithic concrete with anchoring system provides resistance to mechanical loads during rotation and waste loading, extends lining service life without repairs, operation at high temperatures above 800°C, respectively, increases the unit performance. It also heats the exhaust gases in the secondary chamber for further thermal treatment (afterburning) at a temperature of at least 850°C to increase efficiency by accumulating heat, as well as minimizing fuel consumption. Heat resistance up to 1300°C.
The afterburning chamber lining consists of
96
98
When choosing an incinerator, it is necessary to follow several mandatory rules.
In fact, we need to calculate two main parameters that we need to burn a particular type of waste. Incineration rate and waste fraction (size at one-time loading).
1. Type of waste (biological, wood, oil-containing, medical, etc.). The required burning rate depends on this parameter. Each waste burns differently!
2. The volume of waste per day in kilograms. This parameter also affects the burning rate.
3. Working shift in hours.
4. The size of the waste fraction in centimeters. This parameter will determine the required size of the boot window.
Here is an example of how you can choose an incinerator for a particular waste.
1. Type of waste - Biological (gastrointestinal)
2. Volume per day - 1000 kg
3. Working shift - 24 hours
4. Size - 1m3 = 0.7 kg of gastrointestinal tract
It turns out that in this case VOLKAN 750, VOLKAN 500. 1000 kg / 24 = 42 kg per hour + Fraction volume and morphology of waste (the gastrointestinal tract is very wet waste and a more productive incinerator is needed) is suitable for us.
You can always contact our specialists for detailed advice and assistance in the selection of equipment by calling 8 (800) 555-59-12 (in Russia for free).
There is no single way to destroy chemical waste, there are 6 ways of disposal, which are used depending on the composition of the scrap.
Methods of medical waste treatment
In most countries that have ratified the Basel Convention of 1992, the rules and regulations for the disposal and transportation of medical waste are based on its provisions, which involves the use of technologies leading to the destruction of about 90% of medical waste and disinfection, followed by the disposal of the remaining 10%. At the same time, many countries, including Russia, still use the method of disposal in special landfills with preliminary disinfection for the disposal of most medical waste.
In the modern world, the main methods of medical waste treatment are:
Chemical disinfection
Chemical disinfection is most often performed using chlorine-containing substances. Chemical disinfection is often combined with mechanical processes, such as grinding or dissolving, to ensure complete penetration of chemicals.
Incineration using incinerators
Incineration is a controlled process of incineration of medical waste in a special furnace (incinerator). Waste intended for incineration in an incinerator cannot be sorted, so all waste is completely destroyed.
Steam sterilization under pressure and at a temperature of more than 100 ° C using autoclaves
Autoclave is a device for steam sterilization under pressure and at a temperature of more than 100 °. The autoclave is used for sterilization of dressings, linen, tools, dishes for bacteriological laboratories, nutrient media for growing microorganisms, etc. Autoclaves can also be used to sterilize medical waste before disposal in a landfill.
The principle of operation of the autoclave is based on an increase in the boiling point of water with increasing pressure.
Medical waste that has been disinfected in an autoclave must be further processed - compressed, grinded or crushed, so that the waste is unidentifiable and cannot be reused for other purposes. After sterilization and compaction, medical waste can be combined with household waste and disposed of in a common landfill.
Using microwaves
The use of microwaves for disinfection of medical waste is one of the recent innovations in this field. Microwave processing can be carried out both stationary and on mobile objects. For this type of disinfection, the waste is usually pre-crushed, then mixed with water and exposed to microwave radiation. The heat and steam generated during processing ensure uniform heating of all waste and effectively neutralize all biological preparations. Shredding reduces the volume of waste by up to 80%, while recycled waste can be disposed of in a conventional landfill.
An alternative method of sterilization of medical equipment, materials and medical waste is sterilization using ionizing, radioactive or infrared radiationThe sterilization effect of ionizing radiation is the result of exposure to the metabolic processes of the cell, while radioactive and infrared radiation, high-frequency vibrations exert their bactericidal effect with the help of heat developed in the treated object. Not all medical waste can be sterilized in this way (some microorganisms are radiation resistant). The risk of personnel exposure, although minimal, is also a disadvantage of this method.
At the moment, there is no separate federal law on medical waste in Russia, where the concept of "medical waste" would be clearly spelled out, rules for their collection, temporary storage, transportation, burial or destruction were contained, responsibility for the execution of each of the stages was determined, as well as measures applied in case of violations.
The rules for the treatment of medical waste are regulated by sanitary rules and norms N2.1.7.2790-10 of December 12, 2010 "Sanitary and epidemiological requirements for the treatment of medical waste".
For more information, please call the toll-free number 8 (800) 555-59-12
Recycling About 40-50% of MSW are subject to repeated processing with the help of special technological equipment. The list of valuable raw materials includes the following types of waste:
All of the above materials can act as secondary raw materials after the processing process. Then they gain a second life in the form of products used in various spheres of human life.
Incineration is the most efficient way of disposal for all types of waste – solid, liquid and gaseous. It is carried out under the influence of extremely high temperatures exceeding the mark of 1000 ° C. The low-temperature combustion process is dangerous for the environment, as a result of which this method is being replaced by new technologies.
Burial is one of the simplest and cheapest options for waste disposal. Burial can be carried out on specially allocated land plots - landfills, quarries. This method of garbage disposal is ineffective and unsafe for the environment.
Result:
The prospects for generating income from the removal, storage, processing and incineration of garbage depend on their initial investments and the list of services provided. Only the collection and removal of solid waste on one unit of special equipment, which will regularly serve 6 - 8 points, can bring up to 6 thousand net profit per night, and 1 kilogram of solid waste in the cost of incineration costs is not more than 1.5 rubles. If there is not one machine, but several incineration plants, if there is at least one sorting line, it will be possible to process valuable scrap or at least just sort it, burn the "tails" after sorting, then the level of income from solid waste disposal activities will increase many times.
In combination, several methods can give maximum efficiency and economic benefits.For more information, please call the toll-free number 8 (800) 555-59-12

Рабочее время 8:00-17:00 (МСК)
Рабочее время 8:00-17:00 (МСК)
Рабочее время 8:00-17:00 (МСК)
Рабочее время 8:00-17:00 (МСК)
Нажимая на кнопку, Вы даете согласие на обработку персональных данных.

